Shell: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
imported>Burghardt |
imported>Burghardt |
||
| (4 dazwischenliegende Versionen desselben Benutzers werden nicht angezeigt) | |||
| Zeile 47: | Zeile 47: | ||
| ⚫ | |||
| − | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| − | ''<small>There used to be some other mechanisms. The only one left currently is "Port knocking"</small>'' |
||
| − | === Rate Limiting === |
||
| − | Usually we do utilize "<tt>fail2ban</tt>" to chase brute force attacks by bad guys trying to hack login credentials. For technical reasons this is not possible for this "<tt>haproxy</tt>" approach. The inconvenient workaround is: |
||
| ⚫ | |||
{| style="border: 1pt black dashed" |
{| style="border: 1pt black dashed" |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| − | | [[Image:Diamond-caution.png]] || We do limit the rate of ''new'' <tt>ssh</tt>- (<tt>tcp</tt>-) connections from |
+ | | [[Image:Diamond-caution.png]] || We do limit the rate of ''new'' <tt>ssh</tt>- (<tt>tcp</tt>-) connections from each source IP address to '''10 per minute'''. If you hit this limit your source IP address is blocked for 5 minutes.<br /><small>The parameters are in flux and may change without further notice.</small>|| [[Image:Diamond-caution.png]] |
|- |
|- |
||
|} |
|} |
||
| − | When you're going to login via ssh you usually have three tries to enter your password. Technically this is just ''one'' single connection! The next three tries come with the next connection, which is only possible after one minute. Trying to to log in too early gives just a generic error message: |
||
| − | ~# ssh username@shell.stud.informatik.uni-goettingen.de |
||
| − | ssh_exchange_identification: read: Connection reset by peer |
||
| − | |||
| − | This behavior should be fine for most users where each one has a different IP address than other people. |
||
| − | |||
| − | If you are a group of students behind NAT this could be a problem. We need yet to find out if this might be a problem for students residential establishment in Göttingen. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
=== Port knocking === |
=== Port knocking === |
||
For security reasons a "port knocking daemon" got installed. It works like a secret knocking sequence at the door of a conspiracy meeting: only after you have successfully performed that secret sequence the door is opened ''for a moment''. In our technical context this means that the listening <tt>sshd</tt> is ''reachable'' '''for 300 seconds''' after knocking... |
For security reasons a "port knocking daemon" got installed. It works like a secret knocking sequence at the door of a conspiracy meeting: only after you have successfully performed that secret sequence the door is opened ''for a moment''. In our technical context this means that the listening <tt>sshd</tt> is ''reachable'' '''for 300 seconds''' after knocking... |
||
| Zeile 155: | Zeile 144: | ||
Before you can use this technology the first time you need to prepare your personal secret credentials. You do this by using a simple command line tool and answering some questions. |
Before you can use this technology the first time you need to prepare your personal secret credentials. You do this by using a simple command line tool and answering some questions. |
||
| − | Of course you can not do this on these shellX-machines as you can not login successfully (chicken-and-egg problem). Use one of the physical pool computers or login.stud.informatik.uni-goettingen.de instead. |
+ | Of course you can not do this on these shellX-machines as you can not login successfully (chicken-and-egg problem). '''Use one of the physical pool computers for this!''' <!-- or login.stud.informatik.uni-goettingen.de instead. --> |
''The following instructions are copy-n-pastable as the commands are relative to anyones <tt>$HOME</tt>-folder. '' |
''The following instructions are copy-n-pastable as the commands are relative to anyones <tt>$HOME</tt>-folder. '' |
||
| Zeile 227: | Zeile 216: | ||
=== Connect to a specific machine === |
=== Connect to a specific machine === |
||
| − | + | If your are using a ''semi-local source address'' from inside Gönet or inside the Institute = <tt>134.76.0.0/16</tt> + <tt>10.0.0.0/8</tt> + <tt>172.16.0.0/12</tt> circumventing the Round-Robin mechanism is possible: connect to a specific port <tt>42000+''n''</tt> with <tt>''n''={1..6}</tt> |
|
For machine number 4: |
For machine number 4: |
||
Version vom 8. Juli 2016, 08:37 Uhr
Usage
Please read #2FA for initial setup. Then simply use SSH to login to this machine:
~# ssh username@shell.stud.informatik.uni-goettingen.de ####### shell.stud.informatik.uni-goettingen.de - login vm: shell5.cip.loc ... Verification code: Password: Welcome to Ubuntu 14.04.4 LTS (GNU/Linux 3.13.0-87-generic x86_64) username@shell5:~$
For Windows: use PuTTY (simple) or Cygwin (more complex and powerful) or any other SSH-implementation.
Target audience
These machines are meant to be used by students. But of course they can be used by any staff members!
For first time users: the only requirement is to logon one single time using one of the (physical) pool computers in our building - this will make you a "known user" to our systems. Additionally you need to walk through #2FA.
Load Balancing
While this term is misleading on this specific installation as it does simple "round-robin". The important point is that you'll get connected to any login machine. This will be the "next" machine one after another and probably not the same one as one session before. If you landed on an overcrowded system simply disconnect/reconnect to use another machine.
Timeout
- The session Timeout is set to 36 hours -- this is the HAproxy related Timeout regarding the TCP connection
- Kerberos/OpenAFS have separate/shorter timeouts, usually 10 hours. Please check with klist. You need to run kinit && aklog when you're approaching timeout
Self defense of these servers = Rate Limiting
2FA
Two Factor Authentication -- required, not optional
Concept
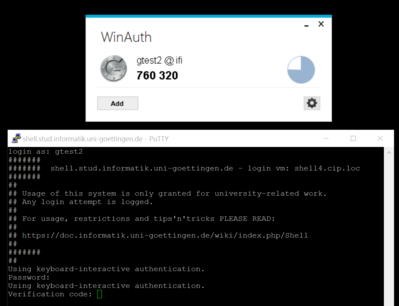
We use the well known google-authenticator to add a second factor as a requirement for (ssh-) logins. First you will get prompted for a "Verification code:". Then you'll get a second prompt asking for your normal "Password:".
The "Verification Code" changes every minute, this approach is called TOTP = Time-based One Time Password.
(Do not try to use "Counter based OTP". It might work first, but it will do so only for a short while! We are using copies of the secret file. State updates required by the incremental counter strategy are not written back. Authentication will fail after reaching the windows size.)
The order of both inputs is relevant: if an attacker manages to crack the first element (being the TOTP) he has a benefit for some minutes only. If we would ask for the Password first then the benefit of cracking the first element gives advantages probably for a very long time.
You need to have a compatible generator - usually implemented as a small application.
Please note that often this approach is associated with a specific implementation: the Google Authenticator. This is misleading as there are other 100% compatible implementations. See also RFC 6238.
Initialization
Before you can use this technology the first time you need to prepare your personal secret credentials. You do this by using a simple command line tool and answering some questions.
Of course you can not do this on these shellX-machines as you can not login successfully (chicken-and-egg problem). Use one of the physical pool computers for this!
The following instructions are copy-n-pastable as the commands are relative to anyones $HOME-folder.
~$ google-authenticator Do you want authentication tokens to be time-based (y/n) y ... # For full output see Shell/2fa-example
Due to some unusual behavior of OpenAFS regarding access rights (they work only on directories, not on files) we need to move that file into another, dedicated subdirectory. This man page explains the access rights mechanism and how to manipulate access-control-lists:
~$ man fs_setacl
First you need to create that directory. A special user with the name ifi-login needs to have read access to the files in the directory .ifi-login inside of your $HOME. To be able to reach into that directory he needs to "walk through" your home folder. The third line is required to make this possible by granting "l"="list" access rights to your $HOME:
~$ mkdir .ifi-login ~$ fs sa -dir .ifi-login -acl ifi-login read ~$ fs sa -dir . -acl ifi-login l
As usual access rights are inherited. For this reason there are more rights granted than required. You might remove them now by commands like
~$ fs sa -dir .ifi-login -acl mta none ~$ fs sa -dir .ifi-login -acl spamassassin none ~$ fs sa -dir .ifi-login -acl web-home none
You can always check the current settings. At the end it may look like this:
~$ fs la .ifi-login Access list for .ifi-login is Normal rights: system:administrators rlidwka username rlidwka username.system rl ifi-login rl # this is the important one (in this context)
WARNING: do not remove rights if you are not absolutely sure they are not needed. It is very easy to remove too many rights, leaving you with a directory that is not usable anymore!
Now move the created credential file into that new destination:
~$ mv .google_authenticator .ifi-login/
Please remember to repeat this step if you modify/recreate your configuration!
Generators
 |
The system time is used equivalent to a shared secret! Make sure your clock is set correctly or all generated codes will fail. |
For all generators you need the secret created above. You can use any tool you want to look into the file .ifi-login/.google_authenticator. A one-liner which outputs only the "secret" is this:
~$ head -n1 .ifi-login/.google_authenticator P2ZOMKQLEIC6SKCL
- Android
- Play Store: "Google Authenticator".
- F-Droid: https://f-droid.org/app/com.google.android.apps.authenticator2
- Linux
- install oathtool to get some compatible command line utilities. Then this works:
~$ oathtool --totp -b $(head -n1 .ifi-login/.google_authenticator) 123456
- Ubuntu Touch
- Authenticator
- Windows:
- WinAuth: https://github.com/winauth/winauth -- direct download as of 06.2016: https://winauth.com/downloads/3.x/WinAuth-3.5.1.zip
This is an installation-free application, no setup and no administrative access needed.
- WinAuth: https://github.com/winauth/winauth -- direct download as of 06.2016: https://winauth.com/downloads/3.x/WinAuth-3.5.1.zip
- OS agnostic
- Chromium Browser: GAuth application
- https://5apps.com/gbraad/gauth -- direct use web-application (think twice!) & application for Chrome and Firefox
Tips 'n' Tricks
Connect to a specific machine
If your are using a semi-local source address from inside Gönet or inside the Institute = 134.76.0.0/16 + 10.0.0.0/8 + 172.16.0.0/12 circumventing the Round-Robin mechanism is possible: connect to a specific port 42000+n with n={1..6}
For machine number 4:
~$ ssh -p 42004 username@shell.stud.informatik.uni-goettingen.de ####### ####### shell.stud.informatik.uni-goettingen.de - login vm: shell4.cip.loc
Duplicate your Generators
It is absolutely fine to have a well configured generator on every single device you own. Remember: without the second factor you can not login. That's the goal of the whole shebang after all.
Write down your Emergency codes
Remember the console output during creation of the secret? "Your emergency scratch codes are:...". Write them down (or print them) and put that piece of paper into your pocket...
Credential problems
- the actual password is not stored anywhere in Institute's systems
- students: StudIT - https://wiki.student.uni-goettingen.de/support/account/passwort
- staff: Gwdg - https://info.gwdg.de/faq/index.php?action=artikel&cat=52&id=215&artlang=de - Institute's Admins will help as we have some administrative access. While we can not tell you your password we can reset it
- problems with the Verification Code: simply start again with #Initialization and overwrite ~/.ifi-login/.google_authenticator. You need to re-configure all of your #Generators of course
Todo
- Testing! -- the current state is considered "BETA"
See also
- Remote Access
- Long Running Processes -- leave processes running
- 2FA/Multiple -- use multiple identities