SL:Introduction
Location
The Sensor Lab is located on the Telematics Group floor, room 1.101 at the IfI. The door is locked by a card reader (Ci-port with profile 0418). Please contact the supervisor of your course to get access to the lab.
Nodes Hardware
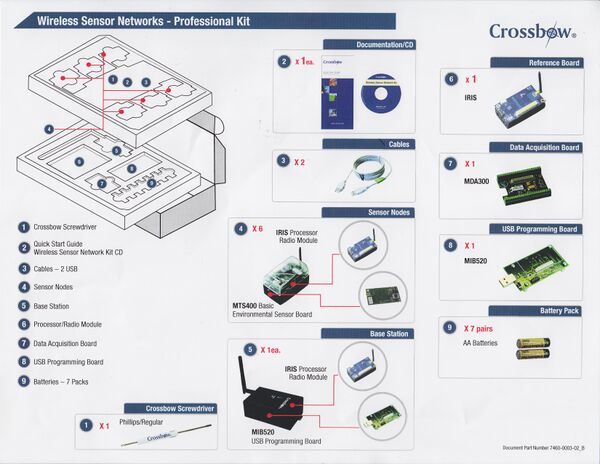
The sensor nodes we have ordered are from Crossbow technology (http://www.xbow.com/Products/productdetails.aspx?sid=264) Basically, the sensors operate in 2.4GHz ISM band. The range of the radio module is about up to 50 m indoor and up to 300 m outdoor.
For more details see the data sheet.
MIB520 USB Gateway boards are available for programming sensor motes, using them with USB power, and debugging or base station uses.
Sensor boards
A number of sensor boards are available.
MDA100CB
A number of MDA100CB sensor boards are available. The include the following features:
- Light sensor: CdSe photo cell
- Temperature sensor: YSI 44006 thermistor
- Prototyping area: For connecting further sensors and devices
MDA300CA
The MDA300CA is a sensor board and general measurement platform. It allows for low-power wireless instrumentation and can be used and extended to be used in various areas.
MTS310CB
The MTS310CB sensor board includes the following components:
- Microphone
- Sounder: 4kHz fixed frequency piezoelectric resonator
- Light sensor: CdSe photo cell
- Temperature sensor: Panasonic ERT-J1VR103J thermistor
- 2-Axis Accelerometer: Analog Devices ADXL202JE
- Two-Axis Magnetometer: Honeywell HMC1002
In addition to the sensors, it also has a sounder, which can be used as an alert, or possibly for audio communication between motes.
MTS400/MTS420
The MTS400CC board, which includes the following sensors:
- Dual-axis Accelerometer: Analog Devices ADXL202JE
- Barometric Pressure Sensor: Intersema MS5534AM
- Ambient Light Sensor: TAOS TSL2550D
- Relative Humidity & Temperature Sensor: Sensirion SHT11
Additionally, a few MTS420CC boards are available, which are basically the same, but include an additional ublox LEA-4A GPS module. Getting this to work with IRIS motes is still a work in progress, however.
A full list of available hardware is also available on the Sensor Lab website. More detailed information is also available.
New motes
A new set of motes and sensors are also available: SL:CM motes
Hardware inventory
The Sensorlab currently has the following motes:
- 1 IRIS mote in a base station case
- 6 IRIS motes with battery section connected by wire (numbered 1-6)
- 30 IRIS motes with fixed battery sections (numbered 7-35 and "Test")
- 3 XM1000 telosb compatible motes (direct USB port; sensors for temperature, humidity and light; bigger EEPROM)
- 6 CM5000 telosb compatible motes (direct USB port; sensors for temperature, humidity and light)
- 3 CM4000 telosb compatible motes
- 4 CM3300 telosb compatible motes (attachable antenna and power)
- 5 CM3000 telosb compatible motes (attachable antenna)
The following attachments are available for IRIS motes:
- 20 MDA100CB sensor boards
- 1 MDA300CA sensor board
- 9 MTS310CB sensor boards
- 6 MTS400CC sensor boards
- 9 MTS420CC sensor boards with GPS antenna attachments
- 11 MIB520 programming boards
The following attachments are available for the telosb compatible motes:
- 9 antennas for CM3000 and CM3300 motes
- 7 power adapters with cables (4 multi-connector)
- 2 MTI USB1000
- 1 MTS EM1000
- 2 MTS DS1000 with SH-300DX sensor attachment
- 2 MTS EX1000 with serial port attachment
- 6 MTS SE1000 with magnetic sensor attachments (one is attached to the window)
- 6 MTS CO1000 with FlexiForce attachments
- 1 MTS AR1000 with two sensor attachments (SH-300DX + PSX-01E)
Most of the new hardware can be found in the bottom most drawer labeled "GPS antennas".
Also available are two SG1000 WSN sinks/bridges.
Waspmote
Raspberry Pi
Additionally, two Raspberry Pi are available, with a working TinyOS setup on both:
- sensorpi1, 192.168.22.50, transparent case, 8GB
- sensorpi2, 192.168.22.51, light gray case, 8GB
Username and password can be found in ~sensorlab/documents/RaspberryPi/info.txt
We also have two CookingHacks Wifi Sets including Raspberry Pi 2: https://www.cooking-hacks.com/wifi-connectivity-kit
There are four additional of the same kits with Arduino instead of Raspberry Pi.
Each of the CookingHacks kits includes four Sugus. These appear to be edible (as yet unconfirmed). Please don't eat all of them and leave some for other people if they are tasty.
NFC
Furthermore, we have an SL:Identive NFC SDK:
- 1 SCL3711 USB NFC reader
- 2 SCM3712 NFC readers with USB cables
- 1 plastic NFC tag
- 2 ISO14443A - TOPAZ 512 NFC sticker tags (crash Linux driver)
- 2 ISO14443A - NTAG 203 NFC sticker tags
- 2 FeliCa Lite S NFC sticker tags
- 2 ISO14443A - MIFARE DESFire EV1 NFC sticker tags
Batteries
We have a number of non-rechargeable batteries, as well as rechargeable AccuCell batteries. Please avoid deep discharges on the AccuCell batteries, as well as unnecessary recharges, as it can significantly lower their lifespan. A map has been placed underneath the transparent battery box, to help identify compartments for freshly charged and used batteries to make management easier.
Documents
TinyOS
General documents can be found on: http://sing.stanford.edu/tinyos-wiki/index.php/Main_Page
TinyOS Iris API: http://www.tinyos.net/tinyos-2.1.0/doc/nesdoc/iris/
How To
How To Disassemble a Sensor Node to Reprogram it (.pdf) (.doc)
Printing
There is a printer in the Sensor Lab, in case you require printed documentation. To use it, please start the ws1 PC, which acts as a print server for the lab. It should be reachable from ws1-6 and pc01.
Modifications for IRIS motes
PacketParrot application
The PacketParrot application which is provided with TinyOS does not work on directly on the Iris motes. Thus, the following modified version can be used instead. The modifications are basically replacing the special radio component, which is used for sending and receiving, by the generic AMSenderC and AMReceiverC components.
Motelist
To make the motelist command work with IRIS motes, a change has to be made to the motelist script. The following patch has to be applied:
--- motelist 2012-11-12 15:23:43.405203257 +0100
+++ motelist.fixed 2012-11-12 15:24:13.326732983 +0100
@@ -62,6 +62,7 @@
# Scan /sys/bus/usb/drivers/usb for FTDI or CP210X devices
my @ftdidevs =
grep { (($_->{UsbVendor}||"") eq "0403" && ($_->{UsbProduct}||"") eq "6001")
+ || (($_->{UsbVendor}||"") eq "0403" && ($_->{UsbProduct}||"") eq "6010")
|| (($_->{UsbVendor}||"") eq "10c4" && ($_->{UsbProduct}||"") eq "ea60")}
map { {
SysPath => $_,
Installation
Debian
SL:Install TinyOS 2.1 in Debian (lenny)
Ubuntu
The PCs in the sensor lab room are currently running Ubuntu 10.04.
TOSSIM
TOSSIM version in Tinyos 2.1.1 requires Python 2.5.5, which is not available in Ubuntu 10.04 (only newer versions are available). The following has been used successfully to install a compatible Python version:
sudo apt-get install build-essential gcc cd Downloads wget http://www.python.org/ftp/python/2.5.5/Python-2.5.5.tgz tar -xvzf Python-2.5.5.tgz cd Python-2.5.5 ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/python2.5 make make test sudo make install sudo ln -s /usr/local/python2.5/bin/python /usr/bin/python2.5 sudo ln -s /usr/local/python2.5/bin/python-config /usr/bin/python2.5-config
VMWare
login to the set up computer
user: wsn password: tinyos
start Xubuntos in VMWare-Player
user: xubuntos password: tinyos
Test
Note: the motelist command does not show any connected motes (I think it is because of that the hardware is very new and therefore cannot be recognised)
To find out which usb device to use, just connect the node and use the dmesg command.
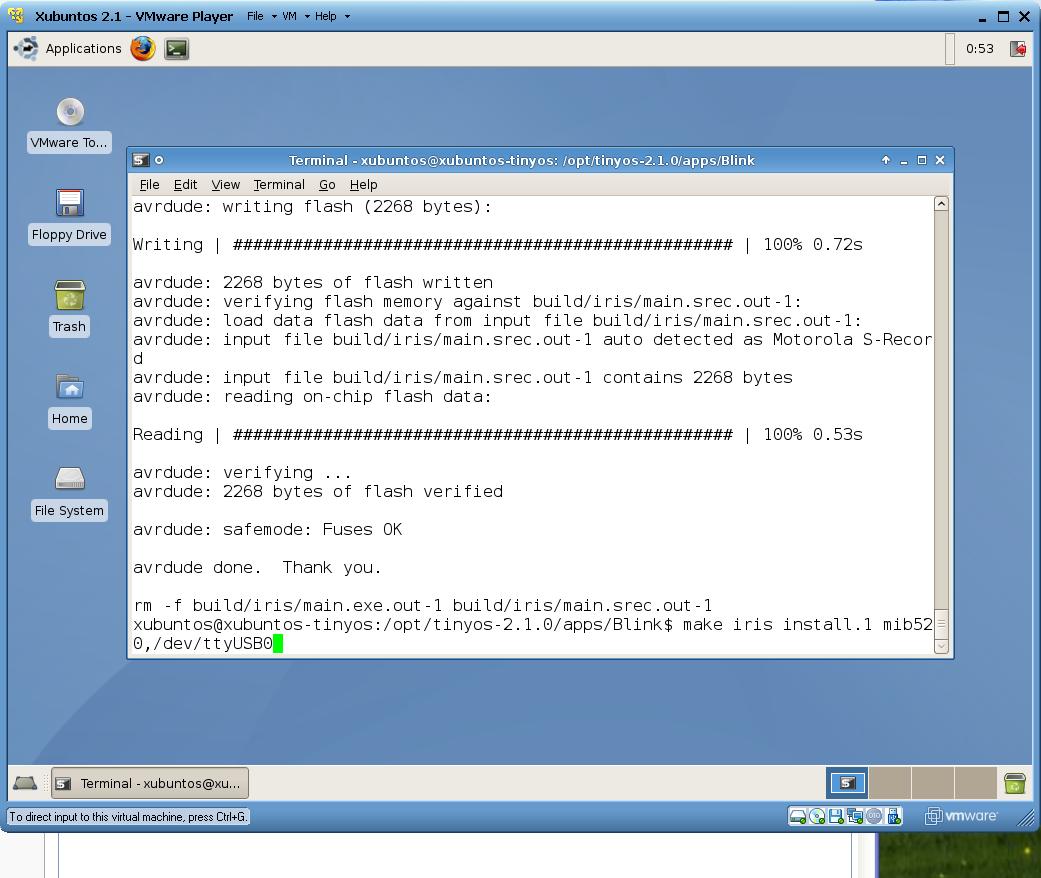
Transfer test application Blink to the node attached via USB
cd /opt/tinyos-2.1.0/apps/Blink make iris install.1 mib520,/dev/ttyUSB0
Manuals (CD KIT)
CD Documents and Manuals
Media:MEP_SYS_Users_Manual_7430-0411-02_A.pdf
Media:MoteConfig_Users_Manual_7430-0112-01_A.pdf
Media:MoteView_Users_Manual_7430-0008-05_A.pdf
Media:MoteWorks_Getting_Started_Guide_7430-0102-01_D.pdf
Media:MPR-MIB_Series_Users_Manual_7430-0021-08_A.pdf
Media:MTS-MDA_Series_Users_Manual_7430-0020-05_A.pdf
Media:TinyOS-nesC_Reference_Manual.pdf
Media:WSN_Quick_Start_Guide.pdf
Media:XMesh_Users_Manual_7430-0108-01_C.pdf
Media:XServe_Users_Manual_7430-0111-01_D.pdf
See also
- SL:Allocation -- list of who uses what hardware and when
- SL:tmg94 -- ESXi Server for hosting Virtual Machines
- SL:PC3 -- local Windows XP
- SL:Virtual Machines
- SL:Remote Access -- reach in from the outside world
- SL:Topology -- the network address ranges, machine names...
- SL:Network_Users
- SL:Power Switches
- SL:CM motes
- SL:Identive NFC
- SL:Waspmote